4WABS Components
IF THE IMAGE IS TOO SMALL, click it. See the NEXT several captions for more...
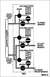
.

For the frame & rear axle lines, see this diagram:

This shows the '93-only SCCDS:

'94-up SCCDS is on the front of the master cylinder, and is the subject of a massive recall.

Reading Diagnostic Codes; Light Flash Technique
1. Note: If 12V test light is not available, the amber ABS warning light also flashes during this test. If it fails to light: locate test connector in the engine compartment and install 12V test light between Pins C and E.
2. With the ignition off, jumper Pin B to E (or any ground).
3. Turn key to RUN position.
4. Remove jumper after 5 seconds.
5. Count light flashes of test light or amber ABS warning light.
Clearing Diagnostic Codes:
All diagnostic trouble codes must be output, all concerns corrected (anti-lock light off) and vehicle driven about 40 km/h (25 mph) before diagnostic trouble codes will be erased.
Note: Do not raise vehicle on hoist and accelerate to 40 km/h (25 mph) to simulate driving the vehicle. Erroneous sensor codes will be set.
Automatic Memory Erasing: A diagnostic trouble code will be automatically erased if no system concerns occur for 50 ignition cycles.
HCU testing
The front isolate valves should read 5-8 Ohms each; all other valves should read 3-6 Ohms each. Sensors should read 800-1400 Ohms across the pins, and more than 10K Ohms from the metal shell to either pin. The pump motor sensor should be 5-40 Ohms.
This site claims to be able to remanufacture the HCU, but when I called in 2021, they said they MIGHT be able to fix the motor ONLY for $300 plus $25 return shipping in about a week. If they couldn't fix it, they'd only charge $35 plus $25sh.
The acceleration sensor is a group of switches which should be closed when the truck is stationary & level. When the sensor is tilted ~1" up in the rear, pins 2-3 should go open; when tilted ~1.5" up in the front, pins 1-3 should go open.

Codes:
11 Possible Source(s):
· Anti-lock brake electronic control module failure.
Action(s) to take:
· REPLACE anti-lock brake electronic control module.
16 Possible Source(s):
· System OK.
Action(s) to take:
· None.
17 Reference Voltage/Intermittent Valve Fault
Possible Source(s):
· 30 amp fuse open.
· Intermittent connections to battery, main relay or ground.
· Main relay coil or contacts open.
· Open or short to ground in Circuit 532 (O/Y).
· Open or short to ground in Circuit 599 (PK/LG).
· Open or short to ground in Circuit 601 (LG/PK).
· Short to ground through anti-lock hydraulic control unit.
· Intermittent valve failures.
· High resistance valves.

22 Front Left Inlet Solenoid Valve Concern Diagnosis
Possible Source(s):
· Intermittent open Circuit 495 (T).
· Terminal backout in anti-lock brake electronic control module connector Pins 17 and 40.
· Terminal backout in anti-lock hydraulic control unit connector Pins 1, 4 and 6.
· Open or shorted inlet front left valve coil.
· Open or shorted driver in anti-lock brake electronic control module.
23 Front Left Outlet Solenoid Concern Diagnosis
Possible Source(s):
· Intermittent open Circuit 496 (O).
· Terminal backout in anti-lock brake electronic control module connector Pins 17 and 26.
· Terminal backout in anti-lock hydraulic control unit connector Pins 1, 4 and 7.
· Open or shorted outlet front left valve coil.
· Open or shorted driver in anti-lock brake electronic control module.
24 Front Right Inlet Solenoid Valve Concern Diagnosis
Possible Source(s):
· Intermittent open Circuit 497 (W).
· Terminal backout in anti-lock brake electronic control module connector Pins 17 and 34.
· Terminal backout in anti-lock hydraulic control unit connector Pins 1, 4 and 8.
· Open or shorted inlet front right valve coil.
· Open or shorted driver in anti-lock brake electronic control module.
25 Front Right Outlet Solenoid Valve Concern Diagnosis
Possible Source(s):
· Intermittent open Circuit 498 (PK).
· Terminal backout in anti-lock brake electronic control module connector Pins 17 and 15.
· Terminal backout in anti-lock hydraulic control unit connector Pins 1, 4 and 5.
· Open or shorted outlet front right valve coil.
· Open or shorted driver in anti-lock brake electronic control module.
26 Rear Axle Inlet Solenoid Valve Concern Diagnosis
Possible Source(s):
· Intermittent open Circuit 499 (GY/BK).
· Terminal backout in anti-lock brake electronic control module connector Pins 17 and 33.
· Terminal backout in anti-lock hydraulic control unit connector Pins 1, 4 and 2.
· Open or shorted inlet rear axle valve coil.
· Open or shorted driver in anti-lock brake electronic control module.
27 Rear Axle Outlet Solenoid Concern Diagnosis
Possible Source(s):
· Intermittent open Circuit 510 (T/R).
· Terminal backout in anti-lock brake electronic control module connector Pins 17 and 27.
· Terminal backout in anti-lock hydraulic control unit connector Pins 1, 4 and 3.
· Open or shorted outlet rear axle valve coil.
· Open or shorted driver in anti-lock brake electronic control module.
31 Left Front Brake Anti-Lock Sensor Diagnosis (Static)
Possible Source(s):
· Poor connection at left front brake anti-lock sensor.
· Terminal damage or backout in anti-lock brake electronic control module connector Pins 24 and 25.
· Terminal damage or backout in two-pin sensor connector.
· Open or shorted left front brake anti-lock sensor.
· Open or shorted Circuit 521 (T/O) or 522 (T/BK).
· Improper front left anti-lock brake sensor cable routing leading to above.
· Defective front left wheel speed sensor electrical test circuit in anti-lock brake electronic control module.
32 Right Front Brake Anti-Lock Sensor Diagnosis
Possible Source(s):
· Poor connection at right front brake anti-lock sensor.
· Terminal damage or backout in anti-lock brake electronic control module connector Pins 36 or 23.
· Terminal damage or backout in two-pin anti-lock brake sensor connector.
· Open or shorted right front brake anti-lock sensor.
· Open or shorted Circuit 514 (Y/R) or 516 (Y/BK).
33 Rear Axle Speed Sensor Diagnosis
Possible Source(s):
· Poor connection at
ABS sensor (DY1123, F85Z-9E731-AB).
· Terminal damage or backout in anti-lock brake electronic control module connector Pins 21 or 22.
· Terminal damage or backout in two-pin sensor connector.
· Open or shorted vehicle speed sensor coil.
· Open or shorted Circuit 518 (LG/R) or 519 (LG/BK).
· Improper vehicle speed sensor cable routing leading to above.
· Defective vehicle speed sensor electrical test circuit in anti-lock brake electronic control module. Note: some vehicles were built using Circuit 523 (R/PK) in place of 518 (LG/R).
35
41
55
75 Left Front Brake Anti-Lock Sensor Diagnosis (Dynamic)
Possible Source(s):
· Damaged/missing front brake anti-lock sensor indicator teeth or missing front brake anti-lock sensor indicator.
· Air gap too small or too large.
· Excessive axle vibration.
· Weak front brake anti-lock sensor.
· Loose front brake anti-lock sensor.
· INTERMITTENT short or open in Circuit 521 (T/O) or 522 (T/BK).
· Disturbances caused by ignition or radio frequency interference.
· Defective trigger circuit in anti-lock brake electronic control module.
36
42
56
76 Right Front Brake Anti-Lock Sensor Diagnosis (Dynamic)
Possible Source(s):
· Damaged/missing front brake anti-lock sensor indicator teeth or missing front brake anti-lock sensor indicator.
· Air gap too small or too large.
· Excessive axle vibration.
· Weak front brake anti-lock sensor.
· Loose front brake anti-lock sensor.
· INTERMITTENT short or open in Circuit 514 (Y/R) or 516 (Y/BK).
· Disturbances caused by ignition or radio frequency interference.
· Defective trigger circuit in anti-lock brake electronic control module.
37
43
57
77 Rear Axle Speed Sensor Diagnosis (Dynamic)
Possible Source(s):
· Damaged/missing indicator ring teeth or missing indicator ring.
· Air gap too small or too large.
· Excessive axle vibration.
· Weak rear axle sensor.
· Loose rear axle sensor.
· Disturbances caused by ignition or radio frequency interference.
· Defective trigger circuit in anti-lock brake electronic control module.
· Intermittent short or open in Circuit 518 (LG/R) or 519 (LG/BK). Note: Some vehicles were built using Circuit 523 (R/PK) in place of 518 (LG/R).
51 Hydraulically Inoperative Front Left Outlet Valve or Sensor Disturbance Detected
Possible Source(s):
· Pinched or closed brake line or hose.
· Worn or clogged front left outlet valve.
52 Hydraulically Inoperative Right Front Outlet Valve or Sensor Disturbance Detected
Possible Source(s):
· Pinched or closed brake line or hose.
· Worn or clogged front right outlet valve.
53 Hydraulically Inoperative Rear Axle Outlet Valve or Sensor Disturbance Detected
Possible Source(s):
· Pinched or closed brake line or hose.
· Worn or clogged rear axle outlet valve.
63 Pump Motor Triggered but Did Not Run
Possible Source(s):
· Damaged pump motor.
· Terminal backout in anti-lock brake electronic control module harness connector Pins 17, 29, 37 and 38.
· Open or shorted pump motor relay coil.
· Open contacts in pump motor relay.
· Terminal backout in pump motor 4-way, Pins 1, 2, 3 or 4.
65 Acceleration Sensor
Possible Source(s):
· Terminal backout in anti-lock brake electronic control module wiring harness connector Pins 30, 31 and 32.
· Worn or damaged acceleration switch.
· Worn or damaged anti-lock brake electronic control module.
· Acceleration switch terminal backout, Pins 1, 2 and 3.
· Short to ground in Circuits 836 (O/W), 886 (O/BK) and 887 (Y).
67 Pump Motor Running but Not Triggered
Possible Source(s):
· Damaged trigger circuit in anti-lock brake electronic control module.
· Terminal backout in anti-lock brake electronic control module harness connector Pins 2 and 3.
· Welded relay contacts.
· Short to ground in Circuit 539 (PK/LB).
-- Amber ABS Warning Lamp On, No Code
Possible Source(s):
· Worn or damaged ignition switch.
· Open ignition feed circuit to anti-lock brake electronic control module.
· Low battery voltage (less than 8V).
· Blown ignition fuse.
· Open system ground.
ABS and Speedometer Are Not Functioning Properly
Possible Source(s):
· No signal to anti-lock brake electronic control module from vehicle speed sensor.
· No signal to speedometer from anti-lock brake electronic control module.
· Defective vehicle speed sensor.
Unwarranted ABS Activity
Possible Source(s):
· Tone ring is damaged.
Action(s) to take:
· INSPECT both front brake anti-lock sensor indicators and the rear axle tone ring.
Possible Source(s):
· Sensor output is weak.
Action(s) to take:
· Left front brake anti-lock sensor -- GO to «Pinpoint Test L».
· Right front brake anti-lock sensor -- GO to «Pinpoint Test M».
· Rear axle sensor -- GO to «Pinpoint Test N».
Possible Source(s):
· Intermittent open or shorted sensor circuit.
· Intermittent open sensor circuit at intermediate connections especially bulkhead.
Possible Source(s):
· Chafed wire insulation or pinched wire due to improper routing causing intermittent short.
Action(s) to take:
· INSPECT wiring harness from front brake anti-lock sensors on knuckle to the frame and from the rear axle to the frame for worn or chafed wire insulation.
Possible Source(s):
· Rear brake adjustment too tight.
· Linings are "grabby".
Wheels Lock Up
Possible Source(s):
· Hydraulic outlet (dump) valve.
· Damp or contaminated rear brake shoe linings, stuck/leaking wheel cylinder, overadjusted rear brakes.
· Hung-up parking brake.
· Leaking rear axle seal.
Hard or Soft Brake Pedal
Possible Source(s):
· Stuck shut inlet (isolation) valve (hard) or leaky outlet (dump) valve (soft).
· Leaky inlet (isolation) valve during ABS (soft).
· Hydraulic leak in brake line or hose, fitting, brake master cylinder, wheel cylinder, or caliper.
· Air in brake system.
· Little or no vacuum boost.
· Stuck or inoperative wheel cylinder or caliper.
· Pinched or crimped brake line or hose.
Lack of Deceleration During Medium/Hard Brake Application
Possible Source(s):
· Stuck shut inlet (isolation) valve or leaky outlet (dump) valve -- rear axle ONLY.
Possible Source(s):
· Hydraulic leak in brake line or hose, fitting, brake master cylinder, wheel cylinder, or caliper.
· Air in brake system.
· Little or no vacuum boost.
· Stuck or inoperative wheel cylinder or caliper.
· Pinched or crimped brake line or hose.
· Ineffective brake shoe or pad linings.
Vehicle Pulls During Braking
Possible Source(s):
· Fully or partially blocked right front inlet (isolation) valve.
· Fully or partially blocked left front inlet (isolation) valve.
· Improperly adjusted rear brake.
· Frozen or binding caliper (one side of vehicle).
· Uneven brake pad or shoe wear.
· Pinched or crimped brake line or hose.
ABS Warning Light On Intermittently with Code 16
Possible Source(s):
· Ignition circuit 601 loose.
· INSPECT Circuit 601 harness from ignition switch to anti-lock brake electronic control module harness connector for opens/shorts especially at the bulk-head connector. CORRECT as necessary.
Possible Source(s):
· Loose anti-lock brake electronic control module grounds.
Action(s) to take:
· INSPECT anti-lock brake electronic control module grounds for looseness, corrosion or excessive dirt. CORRECT as necessary.
Possible Source(s):
· Loose power log at power distribution box.
Action(s) to take:
· CORRECT and REPAIR as necessary.
Possible Source(s):
· Low battery/charging system.
Action(s) to take:
· VERIFY ABS warning light does not come on at idle with high electrical loads.
Light Truck 4-Wheel ABS
A new light truck 4-Wheel ABS was introduced as standard equipment on the 1993 Explorer and Bronco.
Although this system shares some of the features of passenger car 4-Wheel ABS and some of the features of light truck Rear ABS (RABS), it has its own unique features, especially when it comes to diagnosing concerns.
Here are some general features of the light truck 4-Wheel ABS, some of which are common to the other systems as well:
- System prove-out at vehicle start-up of the light truck 4-Wheel ABS is the same as for passenger car and 4-Wheel light truck ABS.
- The amber anti-lock warning light will come on as soon as the vehicle is turned on or started to verify bulb operation, and will go out after 2-3 seconds, provided everything is normal.
- The 4-Wheel ABS operates in 4 x 4 as well as 4 x 2.
- In ABS mode, the brake pedal will pulsate and the pump motor noise may be heard from the engine compartment.
- When ABS codes are read out, code 16 will be present if the system is OK. This code is similar to the EEC's code 111. It basically means that the 4-Wheel ABS Electronic Control Unit (ECU) is indicating that everything is functioning properly electrically. In other words, the components, such as the pump motor and the valves, will activate when needed.
- Conventional bleed is all that is required for service on the new 4WABS including unhooking brake lines from the hydraulic controller (HCU). However, if the HCU is replaced, a special "bleed box" and electrical jumper will be required to bleed the replacement HCU. This procedure is not the same as for the passenger car systems.
There are differences between the Rear ABS and the light truck 4-Wheel ABS.
Front Wheel Control
In the 4WABS system, the front wheels, are now also under ABS control. This is accomplished by adding sensors at each front wheel while maintaining the rear axle
ABS sensor (DY1123, F85Z-9E731-AB) that has been used since 1987 for light truck Rear ABS.
Open vs Closed Systems
There is an important difference in how the 4-Wheel ABS handles a low fluid condition and reacts to the red brake warning light.
RABS Open System
The Rear ABS is what is called an "open" hydraulic system. When an ABS stop is initiated and wheel lock is detected, the isolation or inlet valve closes, preventing any more fluid from going to the rear wheels.
Then, if necessary to prevent lockup, an outlet or dump valve opens to bleed fluid out of the rear brake lines. That fluid goes to an accumulator and is held there for the remainder of the stop.
In RABS "open" system, if there is a low fluid condition and the red warning light comes on, the ABS electronic control unit will detect this condition, turn the amber ABS warning light on and disable the system. The vehicle operator will still have basic brake system performance, but the benefit of RABS is lost.
The reason for disabling the RABS is that the low fluid condition could be caused by a leak in the brake system, decreasing its performance.
4WABS Closed System
In the 4-Wheel ABS the red brake light is not monitored. This is because the system is a "closed" hydraulic system.
If you are in a 4WABS stop and a wheel goes to lock, the isolation valve will activate, just as with the RABS. No more fluid will be directed to the wheel that may lock up.
If it still appears that a wheel is going to lock, the dump valve will open, allowing the fluid to bleed to an accumulator similar to the one in the RABS.
However, in this "closed" 4-Wheel ABS there is a pump that will move fluid from the accumulator, back to the line between the master cylinder and the hydraulic control unit, where it may be recycled again through the isolation and dump valves.
Since the fluid in this closed system is still available to both front and rear circuits, the number of cycles is unlimited. The closed 4WABS isn't shut down when the low fluid light comes on, as was the case with the open system.
Stoplamp Switch Signal
The new 4WABS uses the signal from the stoplamp switch (located on the brake pedal) differently than RABS. RABS is turned on when it receives a signal from the stoplamp switch indicating that the brakes are applied. 4WABS is already turned on and will activate when impending wheel lockup is detected. 4WABS first looks at the wheel-speed sensors. If a wheel appears to be going to lock, the system will activate the ABS with or without the stoplamp switch signal.
