IAC solenoid valves
The Air Bypass (ABP) Solenoid/Idle Air Control (IAC) valve is used to control engine idle speed and is operated by the Electronic Engine Control (EEC) processor. Battery voltage is supplied through the EEC Power relay to the Red wire; the EEC pulses the other wire (White or W/LB) to ground to vary the valve opening.
IF THE IMAGE IS TOO SMALL, click it.
Key off, IAC solenoid disconnected, resistance through the IAC pins should be between 6.0 and 13.0 ohms. Resistance from either pin to the case should be greater than 10Kohms.
NOTE: Due to diode in solenoid, place DVOM(plus) lead on VPWR pin (near connector catch) and (-) lead on IAC pin (near index notch of connector shell.
Hitachi Idle Air Control Valve Recommended Cleaning Procedure
CAUTION: This cleaning procedure may be used with sludge tolerant bodies which are identified with a yellow/black "attention" label. No attempt should be made to clean the throttle body bore/plate area by directly spraying or scrubbing. Do not run engines with airflow meters during the cleaning procedure.
1. Plug the Rotunda Air Bypass Valve Actuator 113-00009 or equivalent into the Rotunda Fuel Injector Tester/Cleaner 113-00001 or equivalent.
2. Remove the air cleaner outlet tube (9B659) to the throttle body (9E926).
3. Disconnect the idle air control valve signal lead.
4. Attach the Rotunda Air Bypass Valve Actuator 113-00009 or equivalent plug to the idle air control valve (IAC valve) (9F715).
5. CAUTION: Do not start engines that have airflow meters. Start the actuator and then start the engine.
6. Spray Carburetor Tune-Up Cleaner D9AZ-19579-BA meeting Ford specification ESR-M14P9-A or equivalent for about five seconds into the inlet passage while the actuator is operating. Avoid direct spraying on throttle plate/bore area.
7. Stop the engine and actuator. Let everything soak for 15 minutes.
8. CAUTION: Do not start engines that have airflow meters. Start the actuator and then start the engine.
9. Spray Carburetor Tune-Up Cleaner D9AZ-19579-BA, meeting Ford specification ESR-M14P9-A or equivalent, into the idle air control valve passage leading to the inlet of the valve for up to one minute. Do not spray for longer than six continuous seconds on engines that have airflow meters and are not running.
10. Stop the actuator and stop the engine if running.
11. Reinstall the air cleaner outlet tube.
12. Start and run the engine for about one minute to dry out the solvent residue.
13. Operate the actuator to make sure the solvent is purged from the idle air control valve.
14. Disconnect the actuator from the idle air control valve.
15. Reattach the control signal lead to the idle air control valve.
16. Check the engine for normal operation.
Alternate Cleaning Procedure for Hitachi IACs
NOTE: Method to be used only when the Rotunda Fuel Injector Tester/Cleaner 113-00001 and Air Bypass Valve Actuator 113-00009 or equivalent for the recommended method are not available.
1. Remove the idle air control valve from the throttle body.
2. Remove the electrical solenoid assembly from the mechanical portion of the idle air control valve by removing the two screws, then sliding the mechanical portion away from the solenoid.
3. CAUTION: Do not exceed three minutes soak time, and do not use choke cleaner as an internal O-ring may begin to deteriorate. Soak the mechanical portion in Carburetor Tune-Up Cleaner D9AZ-19579-BA meeting Ford specification ESR-M14P9-A or equivalent for two to three minutes maximum.
4. With the mechanical portion completely submerged, shake in all directions: up, down, right and left. Then push in on the rod that mates with the solenoid assembly, and again shake in all directions with the unit submerged and the rod held in as far as possible.
5. Remove the unit from the cleaning fluid and dry out thoroughly using shop air.
See also:

Idle Air Trim
Idle Air Trim is designed to adjust the Idle Air Control (IAC) calibration to correct for wear and aging of components. When engine conditions meet the learning requirement, the strategy monitors the engine and determines the values required for ideal idle calibration. The Idle Air Trim values are stored in a table for reference. This table is used by the PCM as a correction factor when controlling idle speed. The table is stored in keep alive memory (KAM) and retains the learned values even after the engine is shut off. A Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is output if the Idle Air Trim has reached its learning limits.
Whenever an IAC component is replaced or cleaned or a service affecting idle is performed, it is recommended that keep alive memory be cleared (disconnect KAPWR fuse or battery for ~3 minutes). This is necessary so the idle strategy does not use the previously learned Idle Air Trim values. It is important to note that erasing DTCs with a scan tool does not reset the Idle Air Trim table.
Once keep alive memory has been reset, the engine must idle for 15 minutes (actual time varies between strategies) to learn new idle air trim values. Idle quality will improve as the strategy adapts. Adaptation occurs in four separate modes. The modes are shown in the following table.
IDLE AIR TRIM LEARNING MODES
Transmission Range - Air Conditioning Mode
NEUTRAL - A/C ON
NEUTRAL - A/C OFF
DRIVE - A/C ON
DRIVE - A/C OFF
Idle Speed Control Closed Throttle Determination
One of the fundamental criteria for entering rpm control is an indication of closed throttle. Throttle mode is always calculated to the lowest learned throttle position (TP) voltage seen since engine start. This lowest learned value is called "ratch," since the software acts like a one-way ratch. The ratch value (voltage) is displayed as the TPREL PID. The ratch value is relearned after every engine start. Ratch will learn the lowest, steady TP voltage seen after the engine starts. In some cases, ratch can learn higher values of TP. The time to learn the higher values is significantly longer than the time to learn the lower values. The brakes must also be applied to learn the higher values.
All PCM functions are done using this ratch voltage, including idle speed control. The PCM goes into closed throttle mode when the TP voltage is at the ratch (TPREL PID) value. Increase in TP voltage, normally less than 0.05 volts, will put the PCM in part throttle mode. Throttle mode can be viewed by looking at the TP MODE PID. With the throttle closed, the PID must read C/T (closed throttle). Slightly corrupt values of ratch can prevent the PCM from entering closed throttle mode. An incorrect part throttle indication at idle will prevent entry into closed throttle rpm control, and could result in a high idle. Ratch can be corrupted by a throttle position sensor or circuit that "drops out" or is noisy, or by loose/worn throttle plates that close tight during a decel and spring back at a normal engine vacuum.
For base idle check & adjustment:
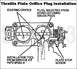
After adjusting the throttle stop, check the TPS range:

The Adaptive Idle Air Control (IAC) strategy is designed to adjust the IAC calibration to correct for wear and aging of components. When engine conditions meet the adaptive strategy learning requirement, the strategy monitors the engine and determines the values required for ideal idle calibration. The adaptive strategy stores these values in a table for reference. This table is used by the PCM as a correction factor when controlling idle speed. The adaptive idle table is stored in Keep Alive Memory (KAM) and retains the learned values even after the engine is shut off. A Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is output to indicate that the adaptive IAC strategy has reached its learning limits.
Whenever an IAC component is replaced or cleaned or a service affecting idle is performed, it is recommended that KAM be cleared. This is necessary so the idle strategy does not use the previously learned adaptive values.
To clear KAM, refer to "PCM Reset" in Section 2A. It is important to note that erasing DTCs with a scan tool does not reset the adaptive idle table.
Once KAM has been reset, the engine must idle for fifteen minutes (actual time varies between strategies) to learn new adaptive values. Idle quality will improve as the strategy adapts. Adaptation occurs in four separate modes. The modes are transmission select in neutral with air conditioning on; transmission select in neutral with air conditioning off; transmission select in drive with air conditioning on; and transmission select in drive with air conditioning off. (See above.)
To find vacuum or exhaust leaks:
